导读
全球气象模型提供了全球范围内的降水预报,有效的降水预报对于农业生产规划和灾害风险管理具有重要意义。近年来,世界主要气象机构相继开发和运行了不同的全球气象模型。美国国家环境预测中心于2011年发布了CFSv2预报模型,美国地球流体动力实验室于2020年发布了SPEAR预报模型。不同的降水预报在全球范围内可能呈现相似的和不同的预报精度。本文基于对确定性系数的集合运算方法,分析了SPEAR和CFSv2全球降水预报的重叠和差异信息。相关结果发表在Science合作期刊Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Research。
研究结果
两套全球降水预报产品与观测的相关系数,如图1所示。整体上,在北美洲西部、南部,南美洲北部,非洲东部和南部,两组预报与观测都有较高的相关性。在欧洲和亚洲中部的一些区域,SPEAR预报与观测的相关性高于CFSv2预报与观测的相关性;相反,在南美洲南部和非洲南部的一些区域,CFSv2预报与观测的相关性高于SPEAR预报与观测的相关性。
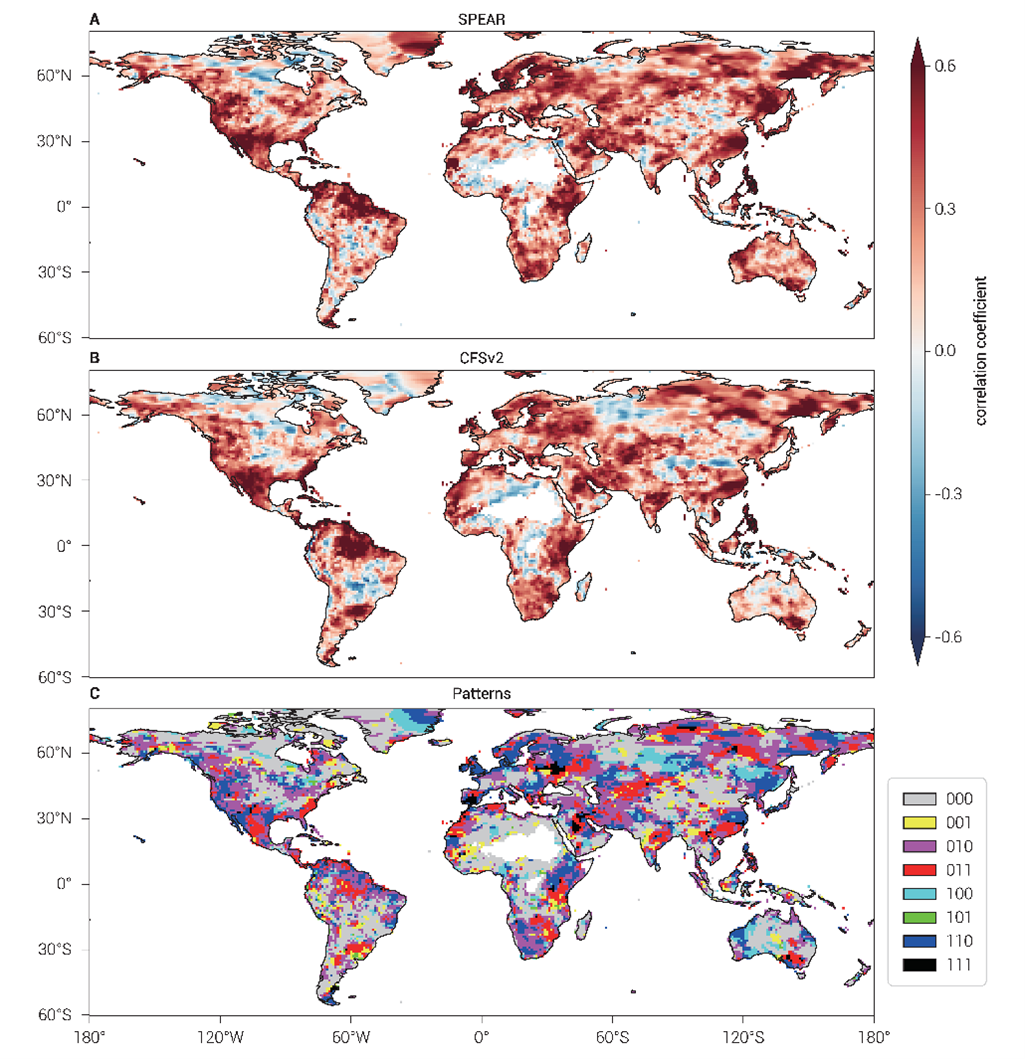
图1. SPEAR预报与观测的相关系数(A),CFSv2预报与观测的相关系数(B)以及二者重叠与差异信息分布(C)
本文基于对确定性系数的集合运算方法量化了SPEAR降水预报和CFSv2降水预报的重叠和差异信息,如图2所示。具体的,以观测降水为因变量,两组预报降水为自变量,构建三组线性回归模型量化两组预报各自解释的降水方差和两组预报解释的总降水方差。进一步,两组预报的重叠信息通过集合的交集运算得到,差异信息通过补集运算得到。在全球的陆地网格单元中,54.61%的网格单元呈现显著的重叠信息,23.59%的网格单元呈现显著的SPEAR预报不同于CFSv2预报的信息,18.15%的网格单元呈现显著的CFSv2预报不同于SPEAR预报的信息。
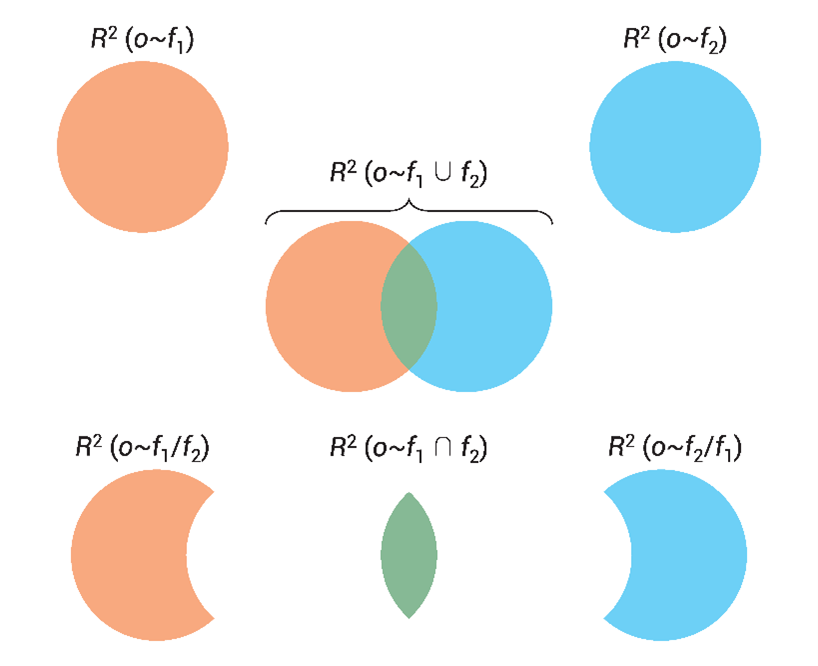
图2. 基于集合运算的重叠和差异信息量化示意图
总结与展望
基于对确定性系数的集合运算方法,本文分析了SPEAR和CFSv2全球降水预报的重叠和差异信息。显著的重叠信息表明两组预报提供了相似的降水信息,而显著的差异信息表明一组预报提供了不同于另一组预报的降水信息。重叠和差异信息的分析可为全球降水预报的评估提供参考。
原文链接:https://spj.science.org/doi/10.34133/olar.0043(点击跳转)
文章标题:Diagnosing overlapping and differing information for SPEAR and CFSv2 global precipitation forecasts
文章作者:Huiling Zhao and Tongtiegang Zhao
文章摘要:
Global climate models (GCMs) provide valuable forecasts of precipitation around the world. This paper has presented an in-depth investigation of the overlapping versus differing information for two sets of GCM forecasts based on the classic set operations. Specifically, by using the coefficient of determination to measure the amount of information of precipitation observations contained in GCM forecast, the common part of the two sets of forecasts is quantified by the intersection operation and the unique part of one set of forecasts is quantified by the difference operation. A case study is devised for the global precipitation forecasts in December-January-February generated by the Seamless System for Prediction and EArth System Research (SPEAR) and the Climate Forecast System version 2 (CFSv2). Their overlapping and differing information are diagnosed. It is found that significant information common to the two sets of forecasts exists over 54.61% of global land grid cells, significant information unique to SPEAR forecasts over 23.59% of global land grid cells and significant information unique to CFSv2 forecasts over 18.15% of global land grid cells. While the information unique to the SPEAR forecasts suggests that the SPEAR forecasts provide new information compared to the CFSv2 forecasts and the information unique to the CFSv2 forecasts suggests that the CFSv2 forecasts also provide new information compared to the SPEAR forecasts, the common information of the two sets of forecasts indicates that they present substantial amount of similar information. Overall, the diagnosis of the overlapping and differing information for different sets of GCM forecasts yields insights into GCM predictive performances.
文章引用:
Huiling Zhao, Tongtiegang Zhao. Diagnosing overlapping and differing information for SPEAR and CFSv2 global precipitation forecasts. Ocean-Land-Atmos Res. 0:DOI:10.34133/olar.0043
第一作者:

赵慧玲,中山大学土木工程学院博士研究生,主要研究方向为水文气象预报。
联系邮箱:zhaohling@mail2.sysu.edu.cn
通讯作者:

赵铜铁钢,中山大学土木工程学院教授,从事流域水文预报、水文气象预报和水资源调度方面的研究和教学工作。
联系邮箱:zhaottg@mail.sysu.edu.cn
OLAR 期刊简介
Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Research (OLAR) 由南方海洋实验室和美国科学促进会合作出版,入选2022年度中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊项目、2024年度广东省高起点英文期刊创办项目,海洋负排放国际大科学计划(Ocean Negative Carbon Emissions, ONCE)学术出版合作平台,已被Scopus, Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) 等15个数据库收录。本刊以海洋相关学科为重点,刊稿主题包括但不限于:海陆气相互作用、海洋碳中和、物理海洋学、海洋生物与生态、海洋地质与地球物理、化学海洋学、海洋气象学、大气物理与大气环境、冰冻圈科学、河口海岸学、海洋工程与海洋技术、海洋资源开发与利用。分享卓见,探索前沿,OLAR 诚邀您一起荟萃科学发现,共享学术盛筵!
期刊官网:https://spj.science.org/journals/olar/
投稿系统:https://www.editorialmanager.com/olar/

扫码关注OLAR微信公众号


