
导读
在全球范围内,沿海地区由于气候变化的加剧而面临着严峻的洪水风险。随着全球温度升高,极端天气事件频繁发生,而沿海地区尤其容易受到其影响。气候变化导致的海平面上升以及人类活动导致的城市化快速发展,大大加剧了沿海城市的洪水风险。因此,对洪水风险和韧性进行系统科学评估,建立有效的洪水风险管理策略至关重要。本文通过综述洪水风险评估和韧性评估的相关文献,提出了一个智慧洪水韧性循环框架,涵盖了洪水灾害全周期的三个阶段(前、中、后)。相关研究成果近日发表至Science合作期刊Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Research。
主要内容
如上所述,全球沿海地区正受到来自气候变化的严峻洪水威胁。极端降雨、飓风和风暴潮等天气事件与海平面上升相互作用,形成了复合洪水事件,给沿海社区的生命、财产和基础设施带来了严重威胁 (图1)。同时,全球城市化的迅速推进,使得许多人口稠密的沿海地区缺乏足够的洪水防护措施,使其更加脆弱。
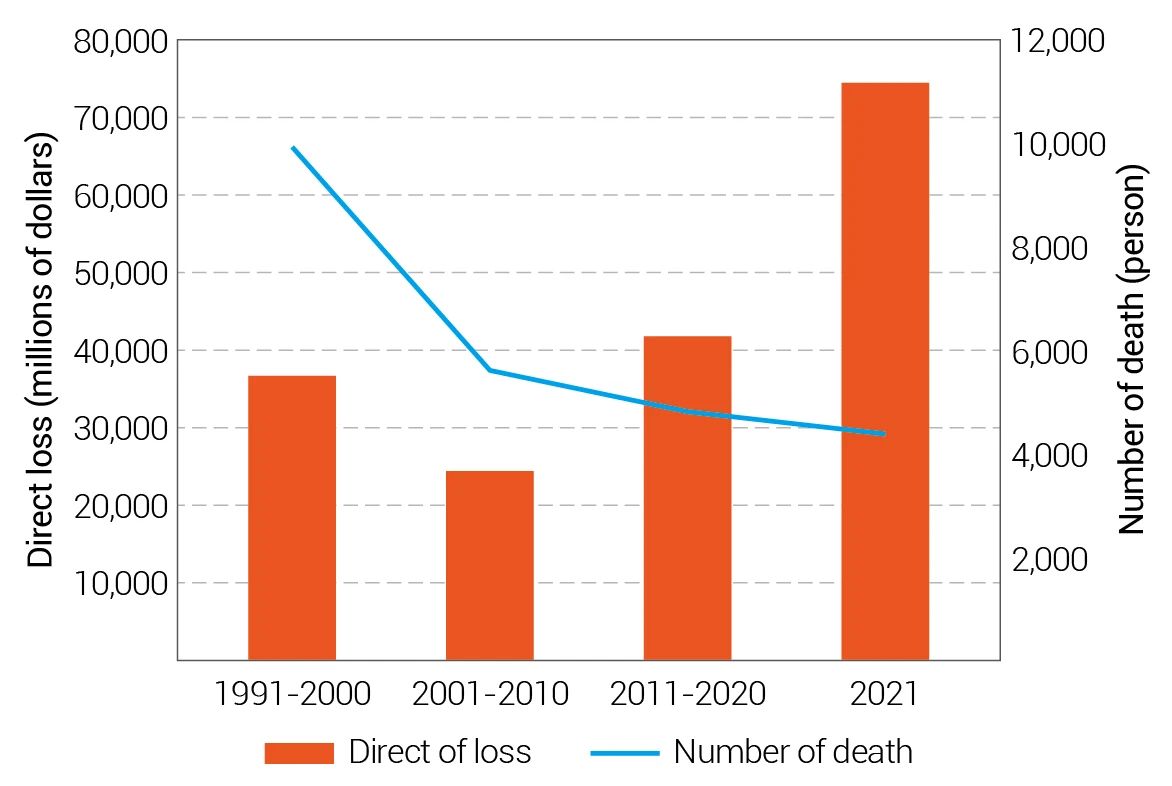
图1 1991年至2020年全球洪水灾害造成的年均损失与2021年损失的对比情况
本文提出了涵盖洪水灾害全周期的三个阶段(前、中、后)的智慧洪水韧性循环框架(图2)。在灾前,风险评估对于全面了解区域或系统的潜在风险至关重要。灾中的大数据监测是有效应急管理和响应的重要组成部分,可以辅助救援抢险决策,从而更迅速、更有效地应对灾害。数据驱动的损失评估可以迅速准确地了解灾后影响,对加速灾区恢复和重建工作起到关键作用。最后,本文总结了气候变化对洪水灾害三个阶段的影响,对于发展更具韧性的沿海社区,使其更能够抵御气候变化的影响并适应不断变化的环境条件,具有重要的意义。

图2 智慧洪水韧性发展框架
总结与展望
本文提出了智慧洪水韧性发展框架,该框架包括三个关键阶段:灾前定量风险评估、灾中利用智能技术进行实时监测和响应、以及灾后损害评估和恢复。为了应对沿海混合洪水风险,研究人员应关注了解致灾因素之间的相互作用、评估经济和社会风险、改进监测和紧急响应系统,并推动具有数据开放性的跨学科研究。这些策略将实现在气候变化背景下全面、整体地管理沿海洪水风险。
原文链接:https://spj.science.org/doi/10.34133/olar.0029
文章标题:
Coastal Flood Risk and Smart Resilience Evaluation under a Changing Climate
文章作者:
Ping Shen, Shilan Wei, Huabin Shi, Liang Gao and Wan-Huan Zhou
文章摘要:
Coastal areas are highly vulnerable to flood risks, which are exacerbated by the changing climate. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the literature on coastal flood risk assessment and resilience evaluation and proposes a smart-resilient city framework based on pre-disaster, mid-disaster, and post-disaster evaluations. First, this paper systematically reviews the origin of the resilience concept and the development of flood resilience. Next, it introduces the social-acceptable risk criteria and the flood resilience level for different flood phases. Then, a coastal flood resilience management system for smart cities is proposed, covering 3 phases of flood disasters (before, during, and after). Risk assessment is essential in pre-disaster scenarios because it provides a comprehensive understanding of the potential hazards and vulnerabilities of an area or system. Big data monitoring during disasters is an essential component of effective emergency management and response that can allow for more informed decisions and thus quicker, more effective responses to disasters, ultimately saving lives and minimizing damage. Data-informed loss assessments are crucial in providing a rapid, accurate understanding of post-disaster impact. This understanding, in turn, is instrumental in expediting recovery and reconstruction efforts by aiding decision-making processes and resource allocation. Finally, the impacts of climate change on the 3 phases of flood disasters are summarized. The development of more resilient coastal communities that are better equipped to withstand the impacts of climate change and adapt to changing environmental conditions is crucial. To address coastal compound floods, researchers should focus on understanding trigging factor interactions, assessing economic and social risks, improving monitoring and emergency response systems, and promoting interdisciplinary research with data openness. These strategies will enable comprehensive and holistic management of coastal flood risks in the context of climate change.
文章引用:
Shen P, Wei S, Shi H, Gao L, Zhou WH. Coastal Flood Risk and Smart Resilience Evaluation under a Changing Climate. Ocean-Land-Atmos. Res. 2023;2:Article 0029. DOI:10.34133/olar.0029


OLAR 期刊简介
Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Research (OLAR) 由南方海洋实验室和美国科学促进会合作出版,入选2022年度中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊项目,海洋负排放国际大科学计划(Ocean Negative Carbon Emissions, ONCE)学术出版合作平台,已被全球最具影响力的开放存取期刊目录DOAJ(Directory of Open Access Journals)数据库收录。本刊以海洋相关学科为重点,刊稿主题包括但不限于:海陆气相互作用、海洋碳中和、物理海洋学、海洋生物与生态、海洋地质与地球物理、化学海洋学、海洋气象学、大气物理与大气环境、冰冻圈科学、河口海岸学、海洋工程与海洋技术、海洋资源开发与利用。分享卓见,探索前沿,OLAR 诚邀您一起荟萃科学发现,共享学术盛筵!
期刊官网:https://spj.science.org/journals/olar/
投稿系统:https://www.editorialmanager.com/olar/

扫码关注OLAR官方微信公众号


