
导读
水汽作为大气中含量最多的温室气体之一,在气候变化和地球系统的反馈机制中至关重要。一方面,水汽对温度有着很强的正反馈,在全球辐射收支平衡中起着关键作用;另一方面,水汽是热带气旋、暴雨等极端天气的重要影响因素。目前,有关水汽气候效应的研究仍存在很多问题,例如,水汽是否会放大温室气体等外强迫导致的气候变化等。为了更好地了解气候系统对温室气体浓度上升的响应,本文利用观测和再分析资料研究了全球对流层水汽的多尺度变率及其影响因子,揭示了全球水汽的长期变化趋势并量化了水汽变化对温度的影响。相关研究成果于近日发表在Science合作期刊Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Research (OLAR) 上。

图1 图形摘要
主要内容
水汽对地球的辐射收支影响巨大,在区域天气过程和气候变化中起着关键作用。本文利用卫星、探空和再分析资料,研究了1980-2020年全球对流层水汽的长期变化,并通过其辐射反馈评估了水汽变化对区域和全球气候的影响。
结果表明,全球水汽分布呈现明显的多时空变率,除热带外,南北半球水汽均存在较强的季节变化,夏季最多,冬季最少。水汽的年际变率受到太平洋十年涛动(PDO)、两极海冰、北大西洋涛动等多种海气因子的联合影响,其中热带主要受厄尔尼诺-南方涛动(ENSO)和PDO的调控。1980-2020年期间,全球多数地区的对流层年平均水汽呈增加的趋势。特别是北极地区,由于增温和北极放大效应,对流层水汽在四个季节均存在明显的增加。
水汽是含量最多的温室气体,水汽的增加将导致地表增温,其相关地面辐射效应在-5 ~ -70 W/m2之间变化,其中Manaus, Porto和Hanty-Mawsijsk(热带站)的辐射效应最强,极地地区最弱。高排放情景预估结果表明,到21世纪末,大气中的水汽含量将大幅增加,其中极地水汽甚至增至当前含量的两倍以上。水汽的增加是全球和区域气候的一个重大挑战,水汽含量的进一步上升将加剧全球变暖和北极放大效应等现象,从而加速全球气候变化。
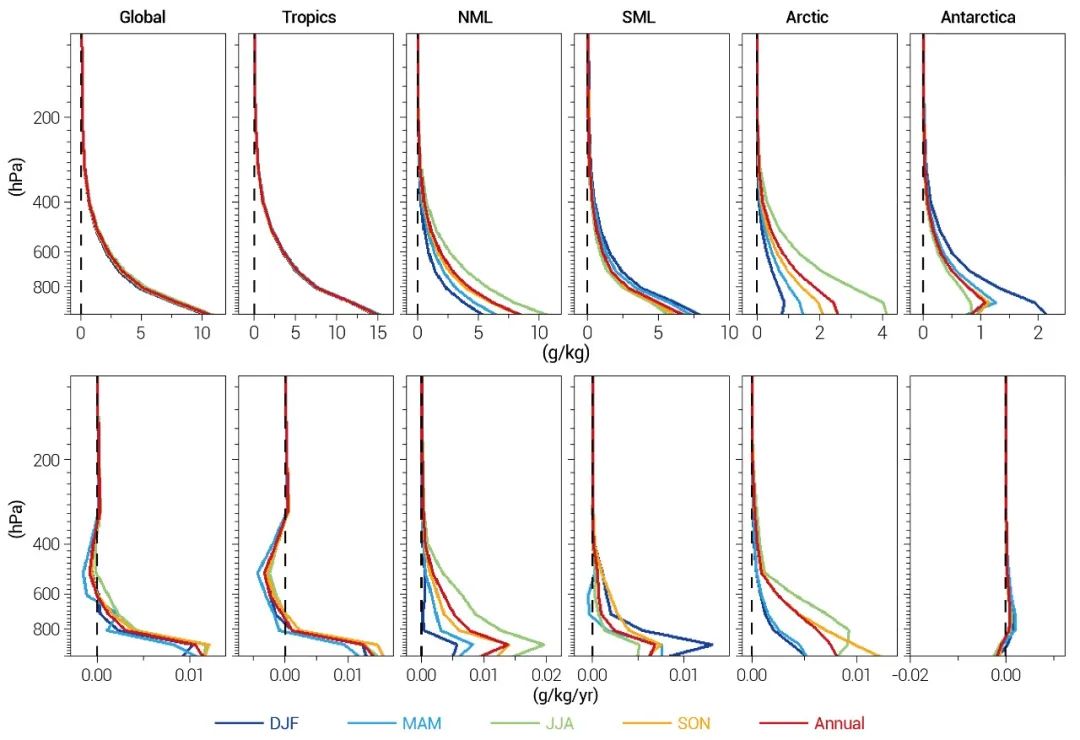
图2 1980-2020年期间比湿垂直廓线(第一行)及其趋势(第二行)。NML和SML分别表示北半球和南半球中纬度地区。第一至五列分别表示全球、热带、北半球中纬度、南半球中纬度、北极和南极。

图3 不同排放情景(Historical,SSP126,SSP245,SSP585)下近地表比湿的变化。
总结与展望
本文利用多种资料,给出了全球对流层水汽的长期趋势,并通过其辐射反馈评估了水汽变化对全球气候的影响。水汽增加会通过其辐射效应导致全球增温,而增温会进一步引起蒸发量和水汽的增加,从而形成正反馈。在高排放情景下,预计到21世纪末,全球水汽将显著增加,特别是极地地区。大气中水汽含量的增加放大了其他温室气体引起的增温效应,这将进一步增强全球变暖,并对全球和区域气候产生不利的影响。本研究提供了与全球水汽增加有关的全球变化的新证据,以便于我们更详细地了解地球气候系统及其对温室气体浓度上升的响应。
原文链接:https://doi.org/10.34133/olar.0015
文章标题:
Increase in Tropospheric Water Vapor Amplifies Global Warming and Climate Change
文章作者:
Vikas Kumar Patel and Jayanarayanan Kuttippurath
文章摘要:
Among the greenhouse gases (GHGs), atmospheric water vapor is the most abundant, has a large influence on the radiation budget of Earth, and plays a decisive role in regional weather processes. We investigate the long-term (1980–2020) changes in global tropospheric water vapor using satellite, radiosonde, and reanalysis data and assess the impact of changes in water vapor on regional and global climate with respect to its radiative feedback. The annual climatology of global tropospheric water vapor varies from 5 to 60 kg/m2 across different regions. Except in the tropics, there is a strong seasonal cycle in both the southern and northern hemispheres, with the highest values in summer (25 to 65 kg/m2) and smallest values in winter (5 to 20 kg/m2). Most regions show positive trends in the annual mean tropospheric water vapor, at about 0.025 to 0.1 kg/m2/year, for the period of 1980–2020, with a notable increase in the Arctic because of the high rise in temperature there. Throughout the troposphere (except 200 hPa), the annual mean specific humidity shows significant positive trends over both land and oceans, with the highest values of approximately 0.015 g/kg/year at 1000 hPa in the tropics. The associated radiative effects on shortwaves at the surface vary from −5 to −70 W/m2, with the highest values at Manaus, Porto, and Hanty–Mawsijsk (tropical stations) and the smallest values of about −5 to −10 W/m2 in the polar regions. The model projections for future high-emission scenarios show a large increase in atmospheric water vapor, approximately twice the current value in the polar latitudes by the end of the 21st century. This is a great concern for global and regional climate, as the rise in water vapor would further augment global warming and phenomena, such as the Arctic amplification. Therefore, this study cautions that there is a significant rise in tropospheric water vapor across latitudes and altitudes, which could further increase the global temperature and, thus, accelerate global climate change.
文章引用:
Patel VK, Kuttippurath J. Increase in Tropospheric Water Vapor Amplifies Global Warming and Climate Change. Ocean-Land-Atmos. Res. 2023;2:Article 0015. https://doi.org/10.34133/olar.0015

OLAR 期刊简介
Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Research (OLAR) 由南方海洋实验室和美国科学促进会合作出版,入选2022年度中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊项目,是海洋负排放国际大科学计划(Ocean Negative Carbon Emissions, ONCE)指定的官方唯一合作期刊。期刊以“服务科学研究,推动技术创新”为办刊宗旨,坚持发表高质量、高水平论文,力争成为具有较大影响力的国际一流学术期刊。本刊以海洋相关学科为重点,刊稿主题包括但不限于:海陆气相互作用、海洋碳中和、物理海洋学、海洋生物与生态、海洋地质与地球物理、化学海洋学、海洋气象学、大气物理与大气环境、冰冻圈科学、河口海岸学、海洋工程与海洋技术、海洋资源开发与利用。OLAR 投稿系统目前已正式开放,热烈欢迎相关研究领域科学家踊跃投稿。分享卓见,探索前沿,OLAR 诚邀您一起荟萃科学发现,共享学术盛筵!
期刊官网:
https://spj.science.org/journals/olar/
投稿系统:
https://www.editorialmanager.com/olar/

扫码关注OLAR官方微信公众号


